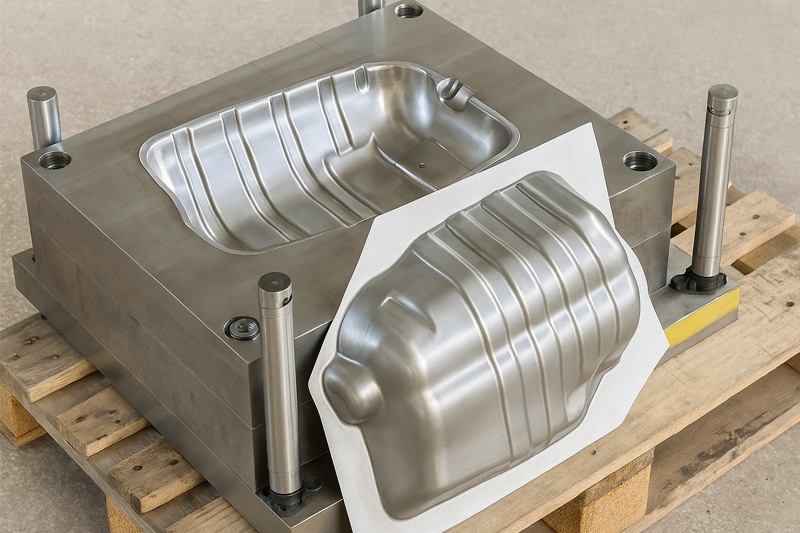
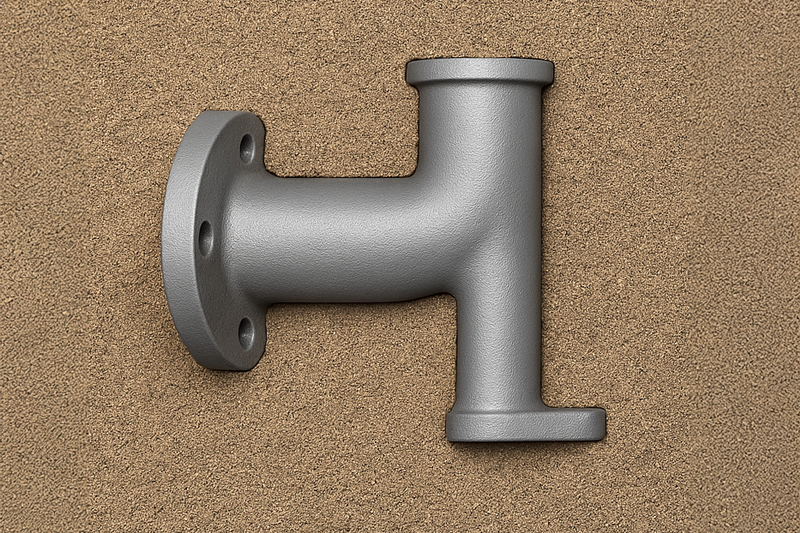
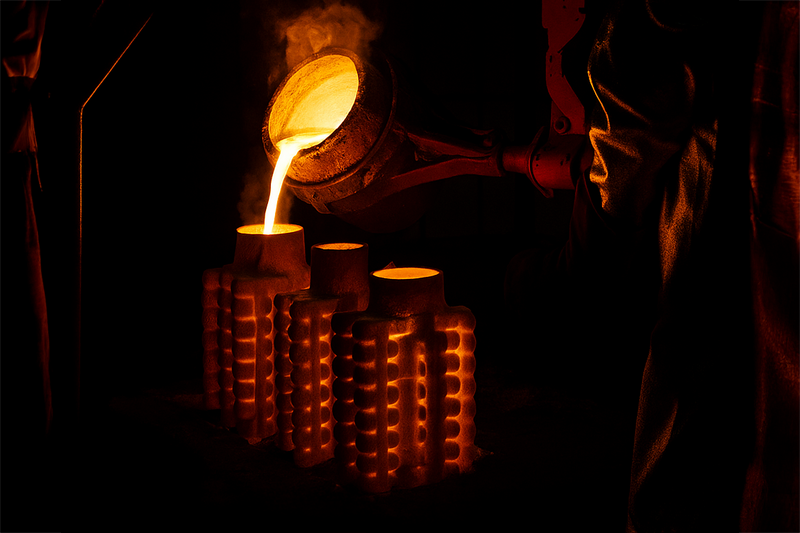Metal casting is a precise metal forming process that produces durable, high-quality components by pouring molten metal into a mold. Before casting begins, engineers design a pattern and the mold is then constructed.
During the casting process, metalworkers heat metals or alloys until they reach a molten state. This liquid metal is then poured into either expendable or permanent molds.
Expendable molds, made from materials like sand or ceramic, are broken apart once the metal solidifies to release the part.
Permanent molds, on the other hand, are designed for reuse and are typically used for simpler shapes that can be easily extracted without damage.
As the molten metal cools inside the mold, it gradually hardens into the desired form. Natural cooling is common, though in some cases water is used to speed up the process once the metal reaches a semi-solid state. For sand-based molds, a vibration step may be included during cooling to prevent sand contamination.
After the casting is complete and the part is removed, additional finishing or cleaning processes are often performed to meet final specifications.
Choosing the right casting method depends on several factors, including part design, material selection, and desired surface finish.